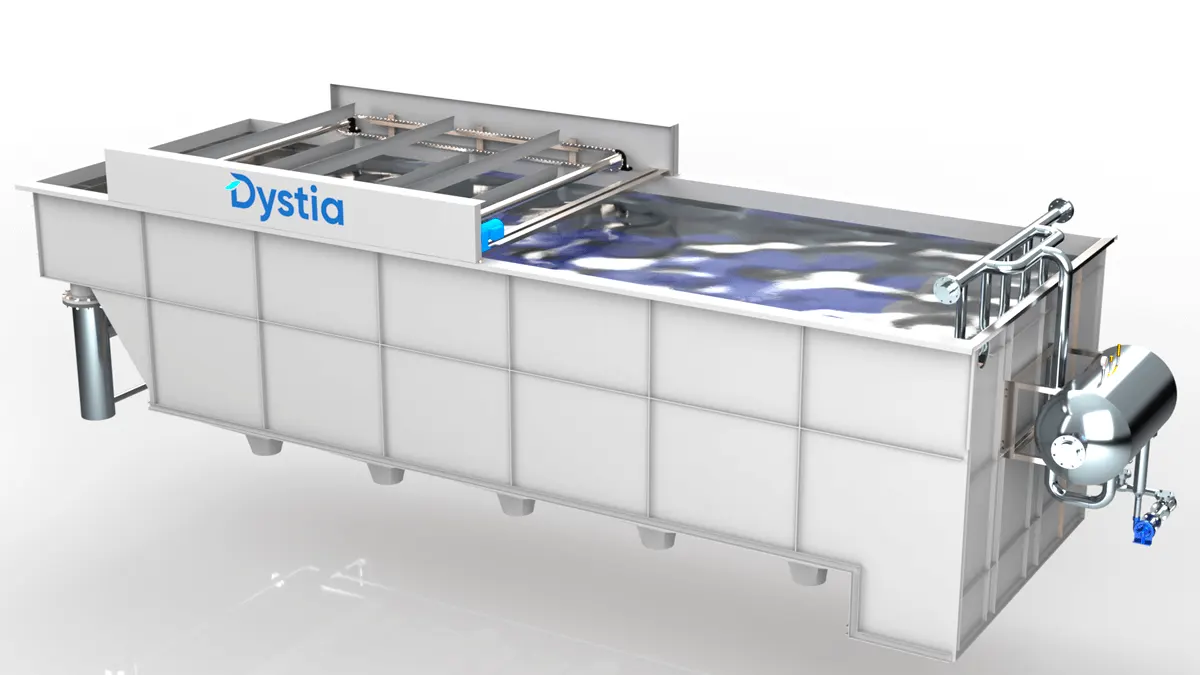
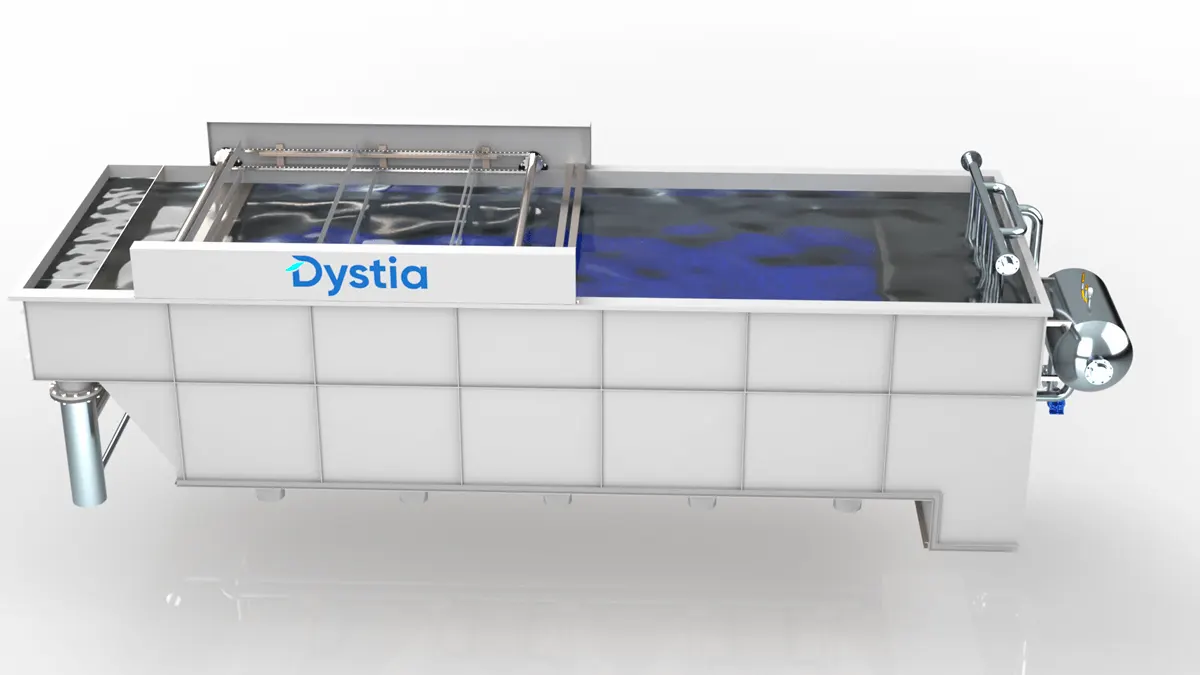
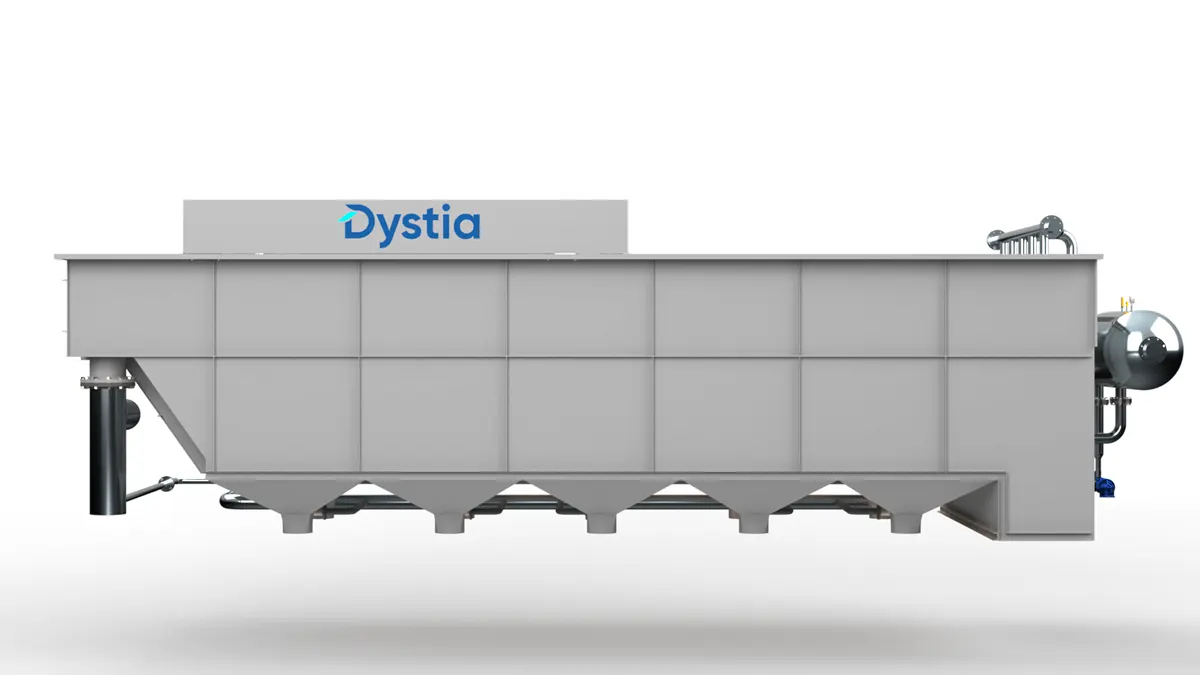
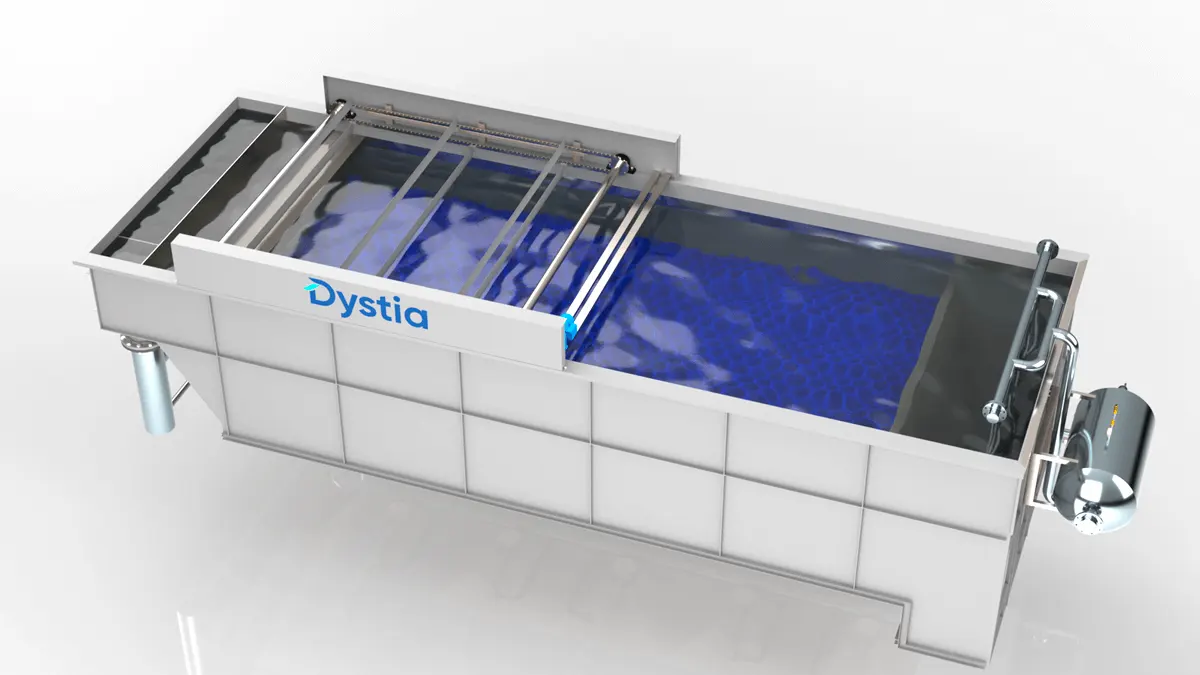
An advanced wastewater treatment that provides efficiency and flexibility
An advanced wastewater treatment mainly used industrially to treat wastewater algae, organics, oil, and grease.
What the DAF process does is to separate suspended contaminant particles from liquids, like oil and grease, by bringing them to the surface of the liquid. These light particles are thus easily removed using physical methods. DAF also facilitates efficient wastewater and process water treatment through flotation with micro bubbles.
The incoming wastewater into a DAF system usually requires pre-treatment. Chemical coagulant(s) and/or flocculant(s) are usually added and the adjustment of pH may also be necessary to ensure optimum operating conditions for DAF.
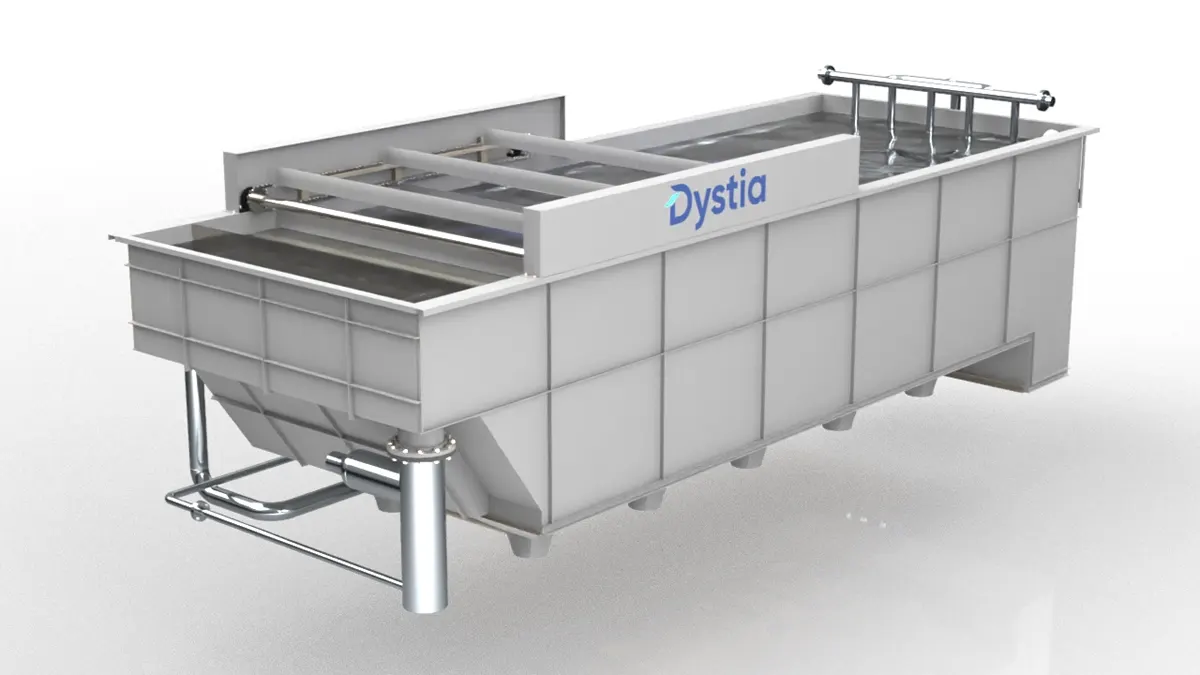

Dissolved Air Flotation: Theory
Dissolved Air Flotation system is an advanced wastewater treatment used mostly in the industrial sector to treat wastewater algae, organics, oil and grease. It is very efficient for the reduction of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) present in fat, grease, oil, biological sludge, coloured organic matter, and colloidal material.It is also excellent for removing oil and grease from industrial wastewater, as mentioned.
DAF has been used for treating drinking water clarification and treatment in several countries like the UK in Europe since the late 1960s and is a common method of choice in drinking water treatment systems in the US too since the 1980s.

DAF Pressure Floatation
Flotation is an extremely critical part of wastewater treatment. In pressure flotation what happens is that air is dissolved in water under high pressure and released at atmospheric pressure through a nozzle or needle valve to produce small air bubbles. These air bubbles then make the lighter contaminants and suspended matter in the wastewater float on to the surface of the water in the flotation tank, and these can easily be removed by a skimming device.
This is the reason, Dissolved air flotation is widely used in treating the industrial wastewater effluents from petrochemicals, oil refineries, and chemical plants where the effluent is made of lighter solids. General water treatments also use DAF for removing colour and organic particles like algae.
Process Efficiency
It gives higher quality effluent that can be safely discharged into the sewer system while fulfilling PCB compliances for industry effluents.
Design and Flexibility
Chemical & Technology
DAF gives the flexibility of multiple chemical sampling and injection points to be included as per the requirements of the effluent
Flotation Tank - For introducing Bubbles
More and more, fish farms face unique challenges in their processing operations, from optimizing water usage to navigating complex guidelines and administrative requirements. Globally, waterwaste treatment became essential for industries. At Dystia, we understand your challenges and offer you comprehensive water waste treatment solutions coupled with expert support to simplify your operations and ensure compliance.